Cleco Pistol Grip Screwdrivers
Clecomatic Clutch
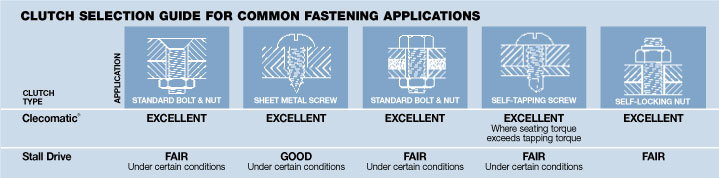
When tightening a fastener, torque is transmitted through the Clecomatic clutch to the fastener until the clutch can no longer transmit the increasing torque. The clutch then "slips", which allows an internal mechanism to seal off air to the air motor, shutting off the tool at the user-adjusted preset torque level. This type of torque controls allows maximum RPM from the tool for increased productivity. Since the tool doesn’t dwell on the fastener as with a stall tool, tool wear and fatigue to the operator is reduced. The life of a Clecomatic tool is up to five times longer than that of a lever-operated, ratcheting clutch screwdriver.

Stall Type
The stall tool doesn’t use a clutch but rather the output spindle is coupled to the last stage of gearing. Torque output from a stall tool may be controlled within fairly reasonable limits with an air pressure regulator. Stall type tools are also trigger activated.
19 Series
Clecomatic Clutch
8 Series
Clecomatic Clutch
88 Series
Clecomatic Clutch
35 Series
Clecomatic Clutch
2 Series
Clecomatic Clutch